| ЙпЧЅЧќНФ : ЦїНКХЭ
|
СЂМіЙјШЃ - 510891 91 |
| Clinical Features of Stress induced cardiomyopathy |
| ыъЕЌъАэЈыІыэыГь ьэъИА ыДъГМ1, ъБДьыэыГь ьэъИА ыДъГМ2, ъВНыЖыэыГь ьэъИА ыДъГМ3 ъГыЊ
ыэъЕыьАьыЃь ьэъИА ыДъГМ4, ыЖьАыьыэыГь ьэъИА ыДъГМ5, ыЖьАыЉыІЌыыГь ьэъИА ыДъГМ6, ьыЈыэыГььэъИА ыДъГМ7 |
| ъЙььА1, ъЙъИАь1, ьЕьЇьЉ1, ьЅьБъЕ1, ъЙъИАь2, ьыэ3, ьБьБьВ 3, ъЙэь4, ьЁАьЄъВН4, ыАээИ5, ьЁАъВНь6 , эъЗИыЃЈ7, ъЙ ь
7, |
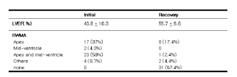
Purpose: Stress induced cardiomyopathy is a syndrome consisted of acute chest pain, ECG changes with elevated cardiac markers and left ventricular wall motion abnormalities in the apical region without coronary artery occlusion or plaque rupture. To assess the clinical and echocardiographic features of stress induced cardiomyopathy, we performed a multicenter retrospspctive enrollment study. Methods: During a nine-year period(1999-2007), we analyzed 46 patients who fulfilled the following criteria: 1) wall motion abnormalities in left ventricular apex or mid-ventricle, 2) absence of obstructive coronary disease or evidence of acute plaque rupture corresponding to region of wall motion abnormalities and 3) absence of recent head trauma, intracranial hemorrhage, pheochromocytoma, and known myocardiopathies. Results: The mean age of patients was 62 years, and 76% of the patients were women. The 12 patients experienced stressful emotional triggers, such as arguments with family members or neighbors(n=4), or death or accident of a family members(n=3). Other 26 patients had physical or disease-related circumstances. Most patients had wall motion abnormalities in the region of apex or mid-ventricle on echocardiography(91%). The left ventricular ejection fraction improved from 40ТБ10% to 55ТБ9%. Conclusions: Stress induced cardiomyopathy has another clinical entity, emotional or physical stress might play a key role in this disease. It has similar to acute myocardial infarction clinically, but more favorable outcome with appropriate therapy. ТБ
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/htdocs/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/scmp2.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





