| єя«•«ьљƒ : јюјЇњђ±ЄјЏїу
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540563 2 |
| Mechanism of Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury assessed by Atomic Force Microscopy and Real time Nitric Oxide measurement system in Rat Myocardium -Cardioprotective effect of Exenatide on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury- |
| к≤љнЭђлМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ, мЭШк≥µнХЩк≥Љ¬є |
| нХШмГБмІД, кєАмЫР,мЭікЄ∞мЮР¬є , л∞ХнЧМкµ≠¬є , мЭімЖМлЭЉ, л∞ХнШДнЭђ, кєАмІДл∞∞, кєАмИШм§С,кєАмЪ∞мЛЭ,кєАл™Ек≥§,кєАкґМмВЉ, л∞∞мҐЕнЩФ |
OBJECTIVE: Mitochondria play critical roles in both the life and death of cardiac myocytes. During ishcemia and reperfusion (IR) injury, Nitric Oxide (NO) metabolism appears complex and NO level in the tissue level has not been assessed up to now.
METHODS: To prove the cardiac protective effect of exenatide and investigate the novel mechanism of heart mitochondria and NO of cardiac protection using morphologic analysis of mitochondria by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and novel technique of real time measurement of nitric oxide (NO) level using NO selective biosensor in the Rat myocardium during IR injury were done and we tested exendin-4 in the concentration range 0.3nM, for their protective effects against IR injury in an isolated rat heart preparation. In-vivo Rat MI model was established by occlusion of the LAD for 40 min and reperfusion for 60 min for showing the mechanism and effect of exenatide on myocardial protection in the IR injury assessed by TTC staning, immunobloting and RT-PCR of RISK pathway, cell survival/apoptotic markers, and eNOS were performed in the infarct border zone.
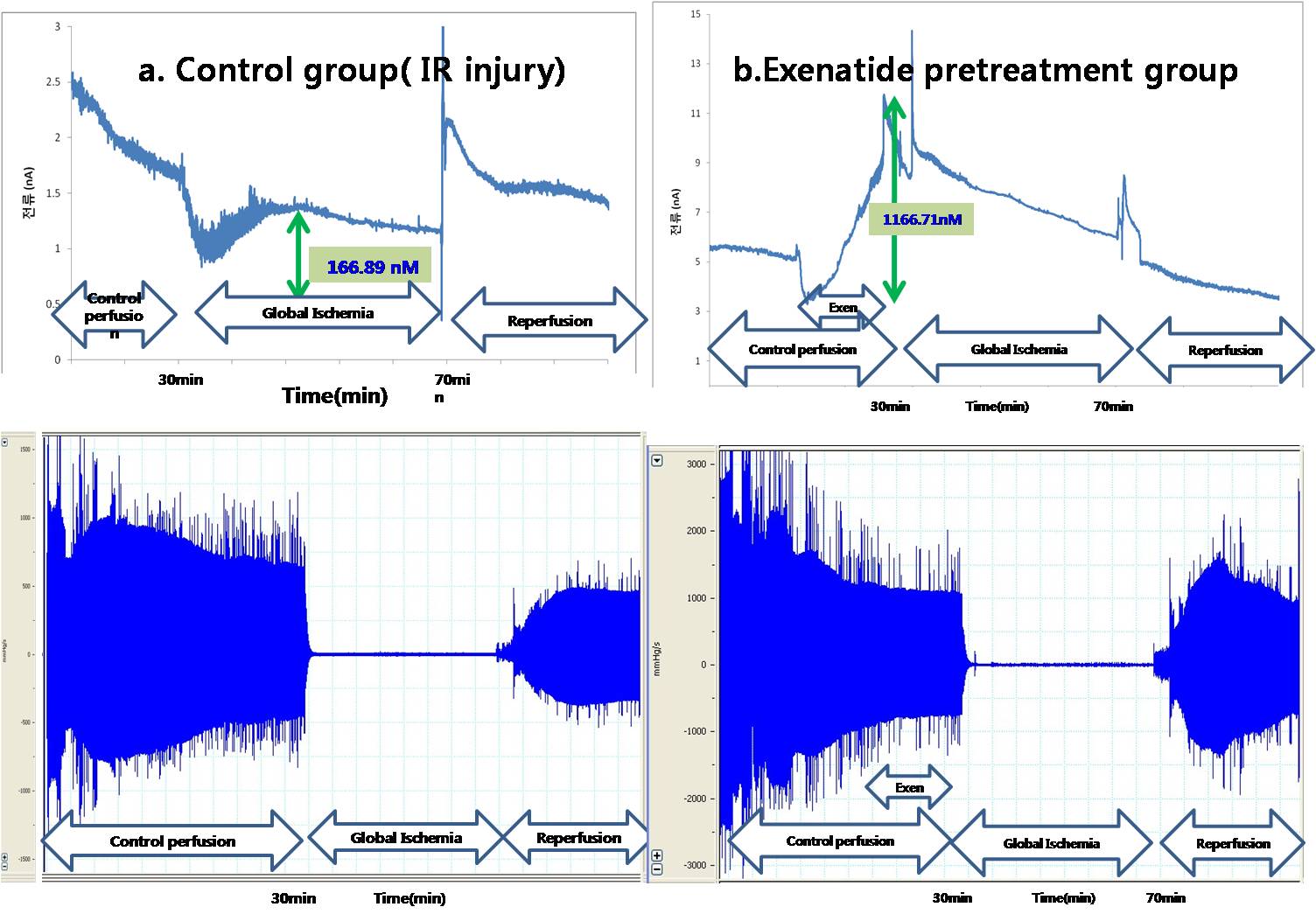
RESULTS: From the shape parameters of mitochondria in AFM topography image, it seemed that myocardial infarction caused the mitochondrial swelling (4,019 ± 1215 nm2 in normal vs 37,859 ± 32381 nm2 in MI, p < 0.0001). As shown in figure 1-a, NO level in myocardium during ishcemia increased by 166.89±150.9 nM, and after reperfusion, temporary increase and plateu curve of NO level was detected. When pretreatment of exenatide before IR, significant increase the NO level by 1,166.71±278.45 nM was detected(Fig1-b). Exenatide reduced myocardial infarct size (35.7±6.4% vs. 53.6±3.9%; p =0.047) as in the previous studies. In addition, molecular work for analyzing mitochondria and NO signaling mechanism of IR injury will be presented.
CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that comparing exenatide pretreatment and control IR exposure rats, NO increase during ischemia contributes to cardioprotective effect.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/NOfig.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





