| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540638 40 |
| Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Single Center Experience |
| к∞Ам≤ЬмЭШлМА мЛђмЮ•мДЉнД∞ мЛђмЮ•лВік≥Љ¬є, к∞Ам≤ЬмЛђнШИкіАмЧ∞кµђмЖМ¬≤, мЛђмЮ•мЖМмХДк≥Љ¬≥, л•ШлІИнЛ∞мК§лВік≥ЉвБі, нШЄнЭ°кЄ∞лВік≥Љ5 |
| л∞ХмШИлѓЉ¬є ¬≤, м†ХмЪ±мІД¬є ¬≤, , мµЬлНХмШБ¬≤ ¬≥, л∞±нХЬм£ЉвБі, м†ХмД±нЩШ5, мЛ†кґМм≤†¬є ¬≤, к∞ХмЫЕм≤†¬є ¬≤, мЛ†лѓЄмКє¬є ¬≤, нХЬмКєнЩШ¬є ¬≤, к≥†кіСк≥§¬є ¬≤, мХИнГЬнЫИ¬є ¬≤, мµЬмЭЄмДЭ¬є ¬≤, мЛ†мЭµкЈ†¬є ¬≤ |
Background and Objectives: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is an orphan disease showing poor prognosis. The purpose of this study was to characterize PAH by evaluating the etiology, clinical and hemodynamic variables and clinical outcomes in Korean.
Methods: A total of thirty nine patients who were diagnosed with PAH at Gachon University Gil Hospital between February 2000 and March 2010 were reviewed retrospectively. The patients with PAH by classification of Dana Point 2008 were included.
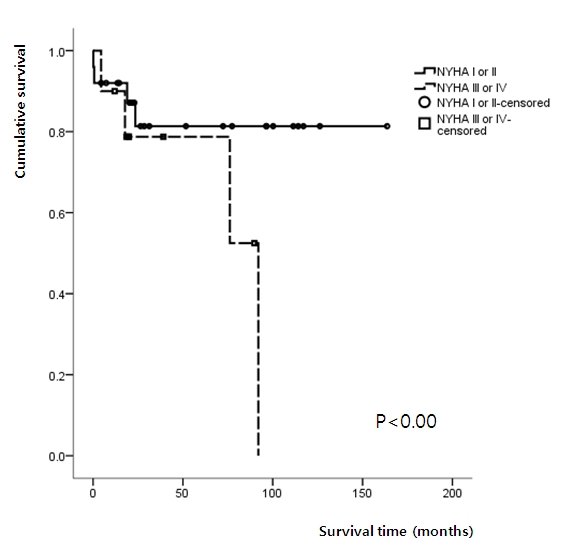
Results: A total 39 patients, 31 patients (79.5%) were female. The median age at the time of diagnosis was 38.0¬±15.5 years and the median follow-up period was 47.0¬±43.3 months. The causes of PAH were congenital heart disease in 21 patients (53.8%), collagen vascular disease associated in 7 patients (17.9%), idiopathic PAH in 5 patients (12.8%), thyroid disorder associated in 3 patients (7.7%) and portal hypertension associated in 2 patients (5.1%) . The most common presenting symptom was dyspnea in 26 patients (66.7%) and 10 patients (25.6%) were NYHA functional classification III or IV at the time of diagnosis. The mean value of right ventricular systolic pressure and mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) by MahanвАЩs equation on echocardiography were 93.1¬±32.9 mmHg and 46.6¬±12.4mmHg, respectively. Seventeen patients (43.6%) underwent right heart catheterization and vasoreactivity test. The mPAP was 56.9¬±16.8mmHg and 3 patient (7.7%) showed response to vasodilator in vasoreactivity test. Eight patients (20.5%) died during follow-up duration and 1-, 2- and 8 year survival rates were 91.4%, 80.1% and 65.2%, respectively. Median overall survival time of patients NYHA functional classification I or II were significantly longer than patients with III or IV. (p<0.00) (Figure 1.)
Conclusion: As reported in other countryвАЩs reports, the NYHA functional classification at time of diagnosis was a one of the most powerful predictors of survival. So, the early screening and referral to the expert center is crucial to improve the prognosis.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/PAHsurvival.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





