| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540685 210 |
| Decreased Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol is Associated with Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction |
| мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА лґАмВ∞л∞±л≥СмЫР¬є, мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА нХімЪілМАл∞±л≥СмЫР¬≤ , мШБлВ®мЭШлМА¬≥ , к≥Дл™ЕмЭШлМАвБі |
| мІДнХЬмШБ¬є, мЮ•мЮђмЛЭ¬є , м°∞мШБмЩД¬є , мЦСнГЬнШД¬є , кєАлМАк≤љ¬є , кєАлПЩмИШ¬є , кєАмЫЕ¬≤ , кєАлПЩкЄ∞¬≤ , кєАмШБм°∞¬≥ , мЛ†лПЩкµђ¬≥ , кєАнШХмД≠вБі , кєАкґМл∞∞вБі |
Background: Although hypercholesterolemia is a well-known risk factor for development of coronary artery disease, it has repeatedly been shown to be associated with lower risk of adverse outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes. We sought to evaluate the impact of decreased baseline low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol level on clinical events in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
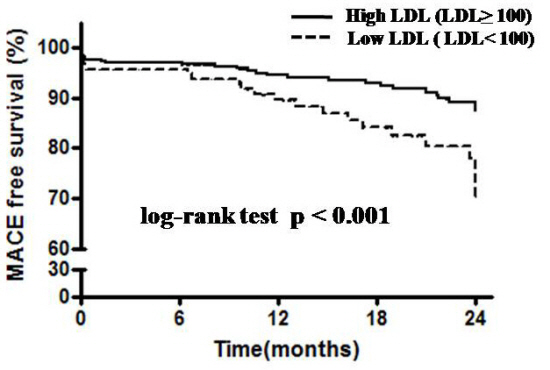
Methods: The consecutive 438 STEMI patients were enrolled from inpatients who underwent primary PCI. Based on the LDL cholesterol levels after primary PCI, patients were classified into two groups: group I: LDL cholesterol < 100 mg/dl (n = 126, 28.8%) and group II: LDL cholesterol вЙ• 100 mg/dl (n = 312, 71.2%). The primary end point was 2-year composite rate of major adverse cardiac events (defined as death, MI, or ischemia-driven target vessel revascularization).
Results: There were no significant differences in baseline clinical characteristics between the two groups, except higher level of C-reactive protein and frequent use of intra-aortic balloon pump in group I. The in-hospital mortality rates were significantly higher in the group I (9.5% vs 1.0%, p <0.001). Similarly, cumulative incidence rates of primary end points in the two groups were 18.3% and 9.0% (p = 0.006). At two year follow-up, the MACE-free survival rates was significantly lower in the group I compared to the group II (p <0.001).
Conclusions: Low baseline LDL cholesterol level was significantly associated with subsequent adverse clinical events after primary PCI in STEMI patients.
Keywords: LDL cholesterol, Myocardial infarction
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/LDL_STEMI.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





