| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540706 205 |
| Standardization of Region of Interest for Speckle Tracking Techniques Improves the Accuracy of Two-dimensional Strain Measurements |
| к∞АнЖ®л¶≠лМАнХЩкµР мЭШк≥ЉлМАнХЩ мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ¬є ,Mayo Clinic Arizona, Scottsdale, AZ¬≤ |
| м°∞мЭАм£Љ¬є, мµЬкЈЬмШБ¬є, кєАлПЩлєИ¬є, мЮ•мД±мЫР¬є, м†ХнХімЦµ¬є, м†ДнЭђк≤љ¬є, мЬ§нШЄм§С¬є, кєАмЮђнШХ¬є, Bijoy K Khandheria¬≤ , Partho P Sengupta¬≤ |
Background: 2D-speckle tracking echocardiography is a novel non-invasive approach to measure left ventricular (LV) deformation. However, variations in tracking algorithms and lack of standardization in data interpretation may produce marked variability of results. We hypothesized that variability in LV strain measurement seen in different tracking algorithms are due to sampling inaccuracies and can be reduced by standardizing the region of interest (ROI).
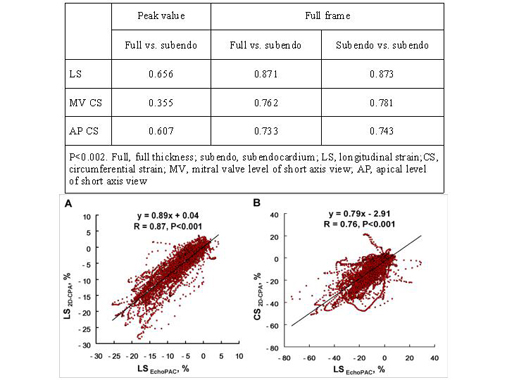
Methods: Total 14,172 LV strain curves were obtained from 74 subjects, including 19 healthy controls (46±18 yrs, 9 male), 17 patients with infiltrative cardiomyopathy (62±9 yrs, 8 male) and 38 patients with cardiac transplantation (57±9 yrs, 26 male). LV strains in longitudinal (LS), radial (RS) and circumferential (CS) directions were analyzed using 2 image analysis platforms (EchoPAC, GE Healthcare and 2D Cardiac Performance Analysis Software, TomTec respectively). Strain curves obtained by both techniques were correlated continuously for the entire cardiac cycle or selectively for peak strains using different ROI (full thickness, selective subendocardial and subepicardial regions respectively).
Results: There were weak correlations for peak strain values when ROI were dissimilar (table). Correlations and limits of agreement were significantly improved with similar thickness ROI and continuous correlation of data points (table, Figure). Analysis of LS and CS curves revealed that the poor correlations resulted from marked variability of data in 33 patients, where higher strains were recorded for ROI restricted to LV subendocardium in comparison with full thickness measurements (-14.2±4.8 vs. -13.6±4.4 %, P=0.05 for LS and -15.0± 5.9 vs. -11.7±3.2 %, P<0.001 for CS at the level of mitral valve).
Conclusions: Transmural heterogeneity of myocardial mechanics results in genesis of nonuniform strain waveforms. Standardization of ROI in speckle tracking algorithms is a key pre-requisite for reducing variability of 2-dimensional strain measurements.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/validationfigure.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





