| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540759 3 |
| Metabolic Syndrome Correlated Not Systolic dysfunction But Diastolic Dysfunction
|
| лМАкµђк∞АнЖ®л¶≠лМАнХЩкµР мЭШк≥ЉлМАнХЩ мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ¬є , лПЩкµ≠лМАнХЩкµР к≤љм£Љл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ¬≤ |
| мД±л™Ем§А ¬є, мЭімІДл∞∞ ¬є, кєАмЖМмЧ∞ ¬≤ , мЭімШБмИШ ¬є, л•ШмЮђкЈЉ ¬є, мµЬмІАмЪ© ¬є, кєА кЄ∞мЛЭ ¬є, мЮ•мД±кµ≠ ¬є |
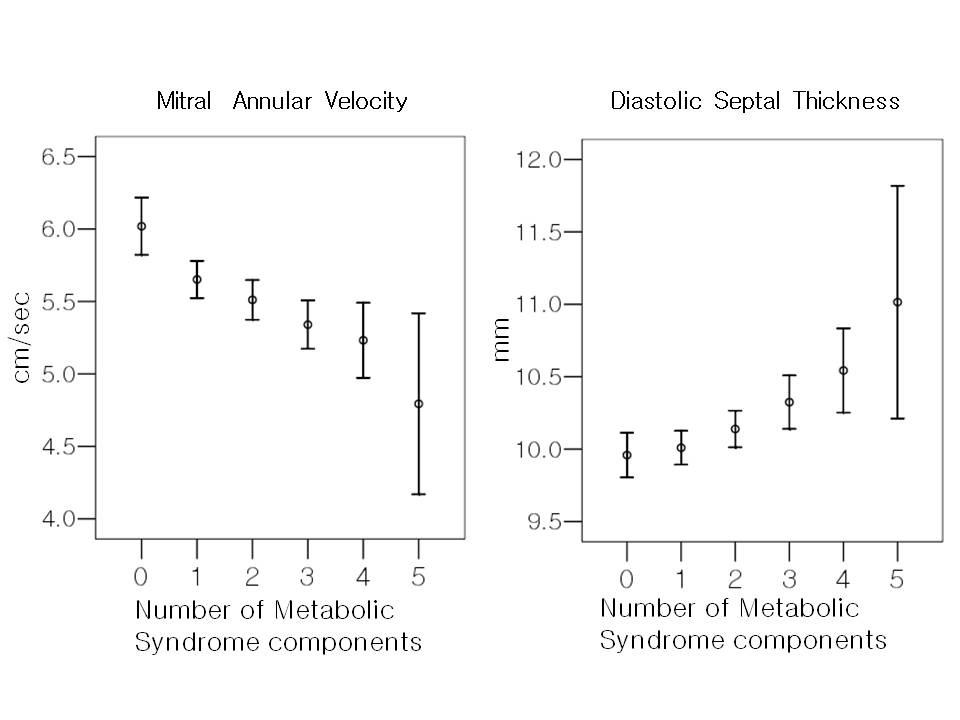
Objiective: Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is associated with increased cardiovascular mortality. But there is limited data about cardiac function. Objective of this study was to investigate the relation between MetS parameter and left ventricle (LV) function. Method: 3875 consecutive patients were underwent 2-dimensional echocardiography and tissue Doppler imaging and evaluation for MetS. Subjects were categorized into six groups according to the number of MetS components present, as defined by the Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Results: MeS do not decrease in systolic fraction, but those with MetS had increased septal wall thickness (10.4 ± 2.2 vs 10.0 ± 2.2 mm, p<0.001), decreased in early diastolic velocity of mitral annulus (Em) (5.3 ± 2.0 vs 5.7 ± 2.4 cm/sec, p<0.001) and increased early transmitral flow velocity (E)/early diastolic velocity of mitral annulus (Em) ratio (15.1 ± 7.9 vs 14.3±7.12, p=0.008) than controls. There was a linear relationship between the number of features of MetS and septal wall thickness (p<0.001 and Em velocity (p<.001). Conclusions: MetS is associated with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction without imparing left ventricular systolic function.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/diastolic2.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





