| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540776 280 |
| Relations of Plasma High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Korean Adults |
| 1 к∞АнЖ®л¶≠лМАнХЩкµР, 2 мЧ∞мДЄлМАнХЩкµР, 3 лґАмВ∞л∞±л≥СмЫР, 4 к≤љнЭђлМАнХЩкµР, 5 к≥Дл™ЕлМАнХЩкµР, 6 к≥†л†§лМАнХЩкµР, 7 мШБлВ®лМАнХЩкµР, 8 мґ©лВ®лМАнХЩкµР, 9 м†ДлВ®лМАнХЩкµР, 10 к≥†мЛ†лМАнХЩкµР |
| л∞±мГБнЩН, мДЬмДЭлѓЉ1, к∞ХмДЭлѓЉ2, кєАлПЩмИШ3, кєАмЪ∞мЛЭ4, кєАнШХмД≠5, лВШмКємЪі6, л∞ХмҐЕмД†7, мД±мЭЄнЩШ8, мХИмШБкЈЉ9, мЬ§м†ХнХЬ2, м†ДнЭђк≤љ1, м∞®нГЬм§А10 |
Backgrounds: Plasma levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) has been known to be a significant predictor for cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease. Of the lipid profiles, low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is more predictive for cardiovascular disease than the others. We investigated to correlate plasma hs-CRP level with cardiovascular risk factors in Korean adults.
Methods: From April 2008 to July 2009, we reviewed 1561 consecutive patients who were tested with hs-CRP level at least once a year. Cardiovascular risk groups were sorted to 4 groups; treatment goal of LDL-C (mg/dl) 70(n=543, 34.8%), 100 (n=223, 14.3%), 130 (n=446, 28.6%), and 160 (n=349, 22.4%), suggested National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guideline. We investigated whether hs-CRP was correlated with cardiovascular risk and its risk factors including age, smoking, hypertension, diabetes, lipid profiles and familial history of coronary artery disease.
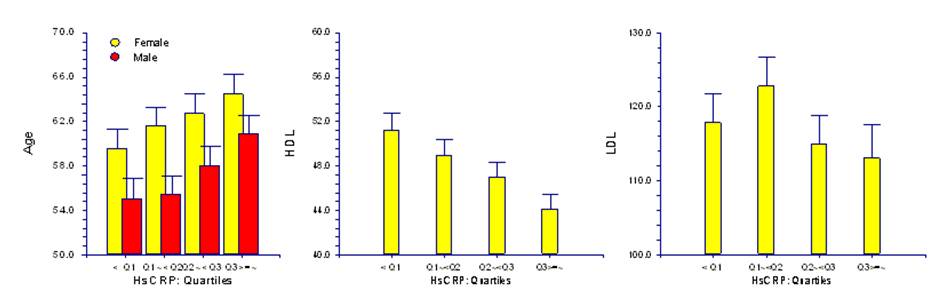
Results: Mean age was 59.6 years, men (n=841, 53.9%) were younger (57.5 vs. 62.0). The mean and median value of hs-CRP (mg/l) was 1.92¬±9.69 and 0.27 (range: 0.01-7.48). Smoking and triglyceride didвАЩt affect the hs-CRP. Men had larger median value of hs-CRP level (p=0.003). When hs-CRP was examined according to LDL-C group, it was significantly increased in each group from high to low group (0.15, 0.23, 0.25 and 0.46 respectively). Hs-CRP was significantly correlated with age (r=0.163, p<0.001), total cholesterol (r=-0.102, p<0.001), LDL-C (r=-0.081, p=0.002), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (r=-0.184, p<0.001) and body mass index (kg/m2) (r=0.050, p=0.048). In the multiple regression for hs-CRP, age, sex, HDL-C and BMI were independently correlated with hs-CRP.
Conclusions: Plasma hs-CRP level is significantly correlated with cardiovascular risk factors and cardiovascular risk of coronary artery disease in Korean adults. Of the lipid profiles, HDL-C is better correlated with plasma hs-CRP more than LDL-C.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/hsCRP.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





