| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540848 83 |
| Clinical Usefulness of Left Ventricular Vortex Flow Analysis for Predicting Symptoms in Patient with Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy |
| мШБлВ®лМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ¬є |
| мЖРмЮ•мЫР¬є, мЭіл≥ік≤љ¬є, мЖРм∞љмЪ∞¬є, мЬ§м§Ам≤†¬є, м°∞нШДмИШ¬є, мЭімГБнЭђ¬є, нЩНкЈЄл£®¬є, л∞ХмҐЕмД†¬є, мЛ†лПЩкµђ¬є, кєАмШБм°∞¬є, мЛђліЙмД≠¬є |
Background: We have frequently seen discrepancies in hemodynamic status and symptoms in patients with apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). Conventional echo-Doppler parameters have limitations for predicting patient's symptoms in patients with apical HCM. The aim of this study was to assess the clinical usefulness of left ventricular (LV) vortex flow analysis for predicting symptomatic status in patients with apical HCM.
Methods: Thirty apical HCM patients were enrolled in this study. Study population was divided into two groups according to symptomatic status including dyspnea on exertion. Of the patients, 14 with symptoms and 16 without symptoms. All patients underwent 2D contrast echocardiography (CE) with intravenous infusion of Definity¬Ѓ (Lantheus Medical Imaging, Inc. North Billerica, MA) and imaged at an mechanical index of 0.4-0.6 in the A4C and APLX views. Quantitative LV vortex flow parameters including morphology and pulsatility were measured using Omega flow¬Ѓ (Siemens Medical Solutions, Mountain View, CA) and compared between two groups.
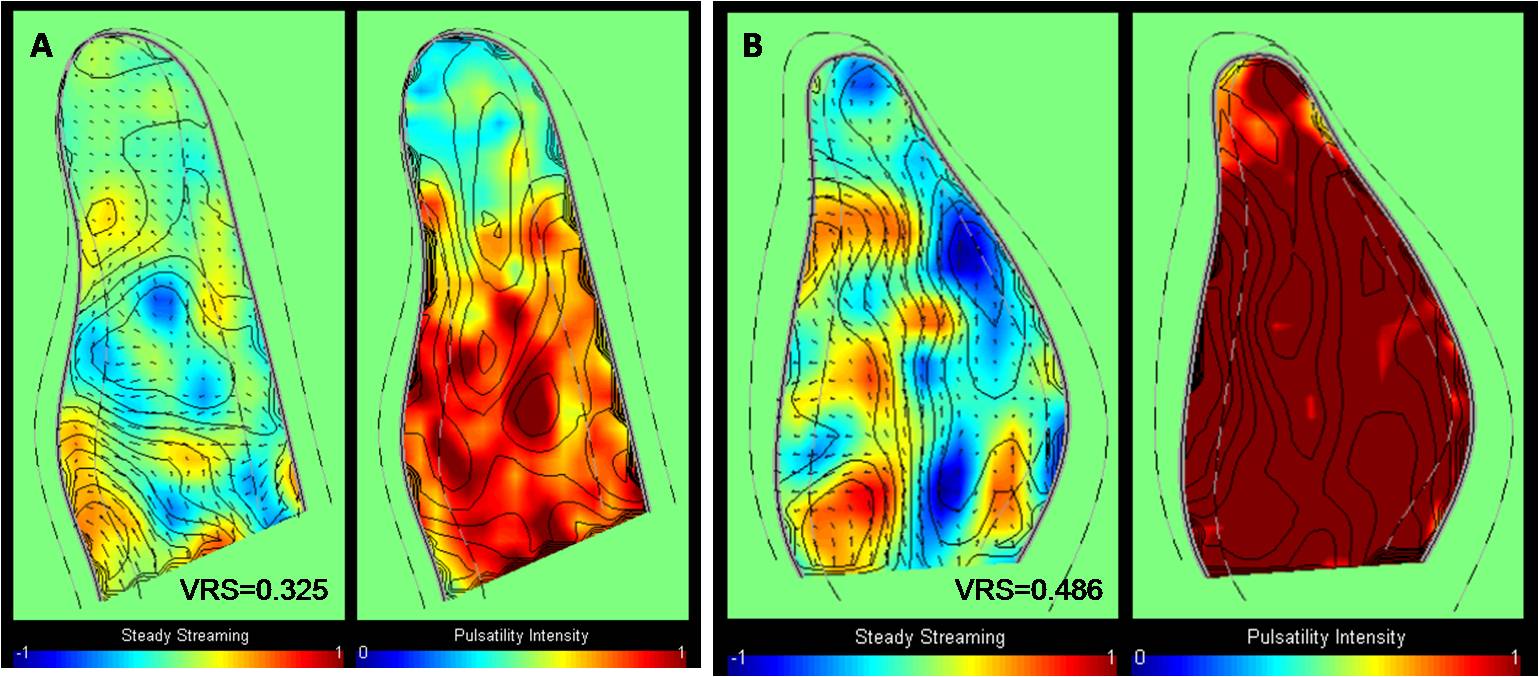
Results: Conventional echo parameters including apical thickness, LV mass index, ejection fraction, LA volume index, and E/E' were not significantly different between two groups. Vortex relative strength (VRS) indicate pulsatility of vortex was significantly lower in symptomatic group compared with asymptomatic group (0.325±0.113 vs 0.486±0.127, p=0.05), however, relative strength (RS) was not significantly different between two groups (2.075 ± 0.450 vs. 2.159 ± 0.308, P=NS). Figure shows parametric representation of steady streaming field (Lt panel) and pulsatile strength (Rt panel) in symptomatic patients (A) and asymptomatic patients (B) with apical HCM.
Conclusion: LV vortex flow analysis is clinically useful for predicting symptomatic status in patients with apical HCM.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/PicturevortexHCMP.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





