| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540857 36 |
| Routine Follow Up Coronary Angiography versus Clinical Follow Up Only following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention with Drug-eluting Stents
: 2-year Clinical Follow Up Results |
| к≥†л†§лМАнХЩкµР кµђл°Ьл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ¬є, мЭДмІАл≥СмЫР мЛђмЮ•лВік≥Љ¬≤, Cardiology Department, the Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China¬≥, Cardiology Department, Nankai Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, ChinaвБі |
| лВШмКємЪі¬є, Kanhaiya L. Poddar¬є, Meera Kumari¬є, л∞ХмІАмШБ¬≤, мµЬл≥Ск±Є¬є, Sureshkumar Ramasamy¬є, Kang Yin Chen¬≥, Yong Jian LiвБі, кєАмЧ∞к≤љ¬є, лВШмІДмШ§¬є, мµЬм≤†мЫЕ¬є, мЮДнЩНмЭШ¬є, кєАмІДмЫР¬є, кєАмЭСм£Љ¬є, л∞Хм∞љкЈЬ¬є, мДЬнЩНмДЭ¬є, мШ§лПЩм£Љ¬є |
Background: There are limited data whether the routine follow up (FU) coronary angiography (CAG) regardless of patientвАЩs symptoms following index percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents (DESs) is beneficial due to early detection of the adverse cardiac events or harmful due to increased repeat PCI by oculostenotic reflex.
Methods: The study population consisted of 1218 consecutive patients (pts) underwent PCI with unrestricted utilization of DESs from November 2005 to June 2008. Routine FU CAG was performed between 6 to 9 months following index PCI and was decided by individual physicianвАЩs discretion. Rests of the pts were clinically followed and ischemic driven events were captured. Pts died before 6 months were excluded in both groups. Cumulative clinical outcomes up to 2 years were compared between Routine CAG group (n=774 pts, 70.4%) and Clinical FU group (n= 325 pts, 29.6%).
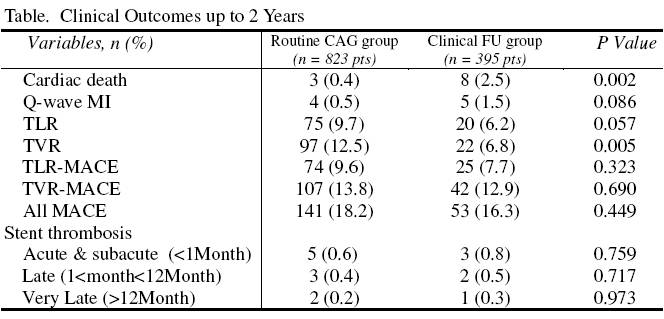
Results: A total 1099 pts (90.2%) were followed up to 2 years. Baseline clinical and procedural characteristics were similar between the two groups except Clinical FU group were older, higher incidence of hypertension, cerebral vascular disease (CVD), previous PCI and lower left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) as compared with those of Routine CAG group. Despite the higher incidence of target vessel revascularization (TVR) and trend toward higher target lesion revascularization (TLR), Routine CAG group showed lower incidence of cumulative cardiac death and a trend toward less incidence of Q-wave MI up to 2 years (Table).
Conclusions: In our study, routine FU CAG following index PCI with DESs was associated with lower incidence of cardiac death and a trend toward less Q-wave MI despite higher chance of repeat PCI due to expected oculostenotic reflex. We suggest that routine FU CAG should be considered to reduce fatal cardiac events in pts undergoing PCI with DESs.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/fff.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





