| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550031 259 |
| Early reperfusion in STEMI influences transmural injury characteristics in cardiac magnetic resonance image and electrocardiographic manifestation
|
| мЛ†міМмДЄлЄМлЮАмК§л≥СмЫР мЛђмЮ•лВік≥Љ |
| кєАлѓЄнШД, нЩ©нШЬмІД,кєАмҐЕмЬ§,мЛђмЮђлѓЉ,мЧДмЮђмД†,м†Хл≥імШБ,л∞ХнЭђлВ®, мЭілђЄнШХ |
Background: Transmural injury in myocardial infarction (MI) has been traditionally regarded to develop Q wave. However, early reperfusion seemes to modify geometry of myocardial fibrosis. Thus, we assesses the hypothesis that early reperfusion during acute myocardial infarction may influence transmural injury patterns cardiac magnetic resonance(CMR) and Q wave manifestations on ECG.
Methods and Results:
Total 34 patients with anterior wall ST elevation myocardial infarction(STEMI) (60.7±11 years, male 82.4%) were enrolled in this study. All underwent CMR and ECG 11.5±15.5days after reperfusion therapy with direct percutaneous coronary intervention(PCI) (n=32, 94.1%) and thrombolytics (n=2, 5.9%). Time to reperfusion (Door to ballooning time ) was 49.35±20.21 min. TIMI flow score after PCI was 2.91±0.29.
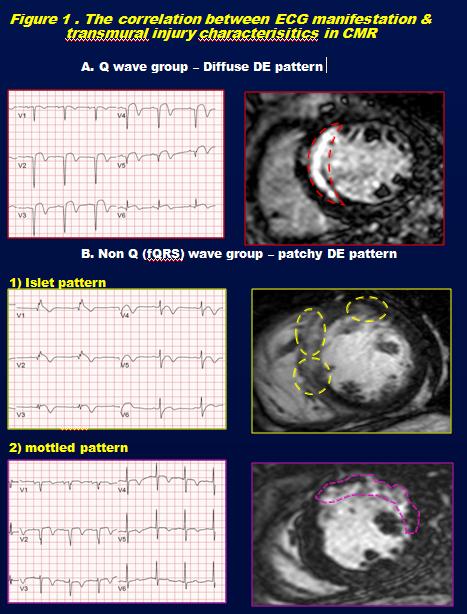
Transmurality pattern in CMR was divided into two types, diffuse and patchy (mottled or islets). Presence of Q wave and fragmented QRS (fQRS) complex in precordial leads were analyzed. All patients showed transmural enhancement in CMR (percentage enhanced area : 32±11%). Q wave was observed in 13(38%) patients and non Q wave group was observed in 21(62%) patients. 12 of 13(92%) patients with Q wave group had diffuse delayed enhancement pattern. All patients with non-Q wave showed patchy delayed enhancement pattern including mottled (n=12, 57%) and islet(n=9, 43%) pattern. 15 of 18(53%) patients with non-Q wave had fQRS complex in V1~V5. Transmurality patterns showed significantly different between Q wave and non-Q wave group (diffuse pattern : 92 % in Q wave group vs patchy pattern : 100% in non Q wave group; p=0.001).
Conclusions:
Transmural injury pattern after early reperfusion was different between the patients with and without Q wave. Early reperfusion influenced the transmurality characteristics and Q wave manifestations.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/circulationSTEMIMR.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





