| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550044 283 |
| Preventive Effects of Exenatide on Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via K ATP Channels |
| к≤љнЭђлМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ, к∞ХлПЩ к≤љнЭђлМАл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ¬є |
| кєАмЫР, нХШмГБмІД, мЪ∞мҐЕмЛ†, кєАмІДл∞∞, кєАмИШм§С, кєАмЪ∞мЛЭ, кєАл™Ек≥§, л∞Хм∞љл≤Ф¬є, мЖРмЭЉмДЭ¬є, мІДмЭАмД†¬є, кєАмҐЕмІД¬є, кєАкґМмВЉ, л∞∞мҐЕнЩФ |
Objective— The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether exenatide administration can prevent impairment in endothelium-dependent vasodilatation induced by ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury and whether this effect is mediated by KATP channel opening.
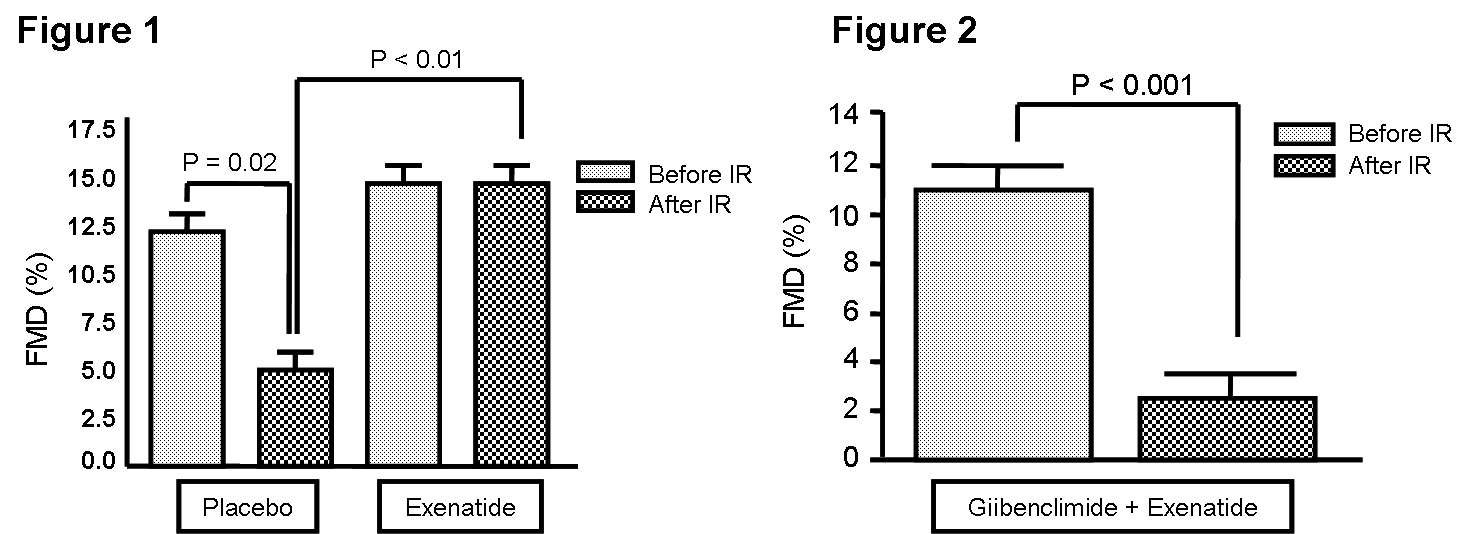
Methods and Results—In a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover design, 20 volunteers were randomized to two groups - subcutaneous exenatide (10 ќЉg) or a placebo administrations. At 30 minute after study drug administration, endothelium-dependent flow-mediated dilatation (FMD) of the radial artery was measured before and after IR (15 minutes of ischemia at the level of the brachial artery followed by 15 minutes of reperfusion) injury. Seven days later, both groups were cross-overed and received the other treatment (i.e., placebo or exenatide) and underwent the same protocol. Pre-IR radial artery diameter, FMD, and baseline radial artery diameter after IR injury were similar between two groups (p = no significant difference (NS)). After placebo administration, IR significantly blunted FMD (before IR: 12.0¬± 6.23%; after IR: 4.6¬± 3.57%, p =0.02). Exenatide prevented this impairment (FMD before IR: 15.0¬±7.14%; FMD after IR: 15.0¬±5.96%, p = NS; p < 0.001 compared with placebo). In a separate protocol, this protective effect was completely abolished by the pretreatment of glibenclamide (glyburide, 5 mg), a blocker of KATP channels (n=7; FMD before IR: 12.0¬±2.2 %; after IR: 3.2¬±2.1 %, p < 0.001).
Conclusions—The present study demonstrates that subcutaneous exenatide protects IR-induced endothelial dysfunction through opening of KATP channels in human IR injury model.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/Peru.png) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





