| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550136 234 |
| Impact of Lesion Length on Chronic Total Occlusion Intervention Outcomes |
| к≥†л†§лМАнХЩкµР кµђл°Ьл≥СмЫР мЛђнШИкіАмДЉнД∞ |
| Amro Elnagar, лВШмКємЪі, мµЬл≥Ск±Є, мЮДмД±мЭЉ, кєАмД†мЫР, лВШмІДмШ§, нХЬмД±мЪ∞, мµЬм≤†мЫЕ, мЮДнЩНмЭШ, кєАмІДмЫР, кєАмЭСм£Љ, л∞Хм∞љкЈЬ, мДЬнЩНмДЭ, мШ§лПЩм£Љ |
Background: Chronic total occlusion (CTO) intervention is still challenging because of the limited procedural success rate and higher target failure. The aim of this study is to evaluate the impact of lesion length on procedure and clinical outcomes.
Methods: A total 250 consecutive patients (pts) who underwent percutanous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents (DES) for CTOs were enrolled for this study. Study population was divided into short lesion group (less than 30 mm, n=123), and diffuse long lesion group (more than 30 mm, n=127).
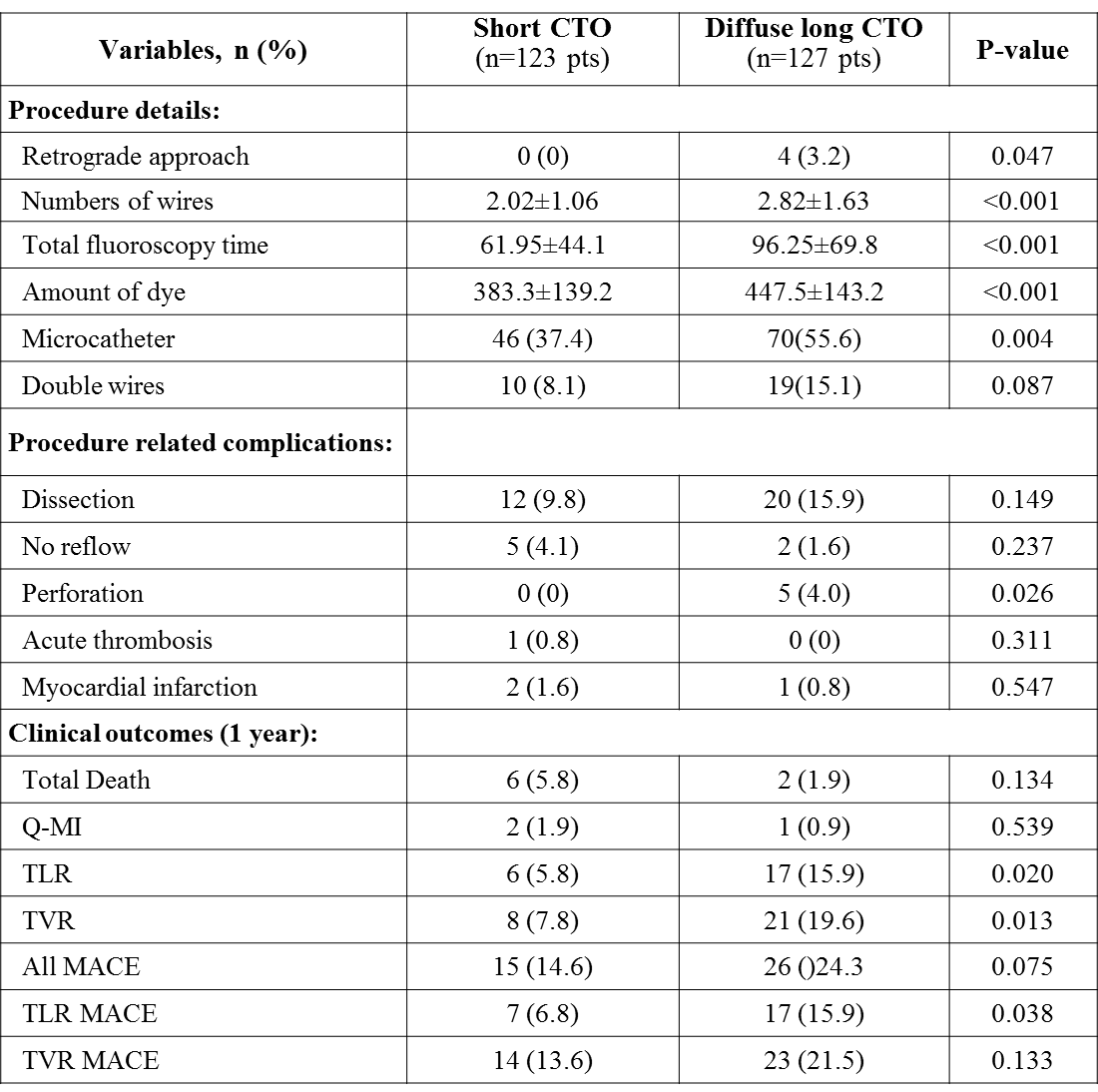
Results: Baseline clinical characteristics & procedure details were similar between the two groups, except pts with diffuse long lesion were more smokers (59.1% vs. 46.3 %, p: 0.044). In long lesion group; use of retrograde approach, numbers of wires, microcatheter, amount of dye and total fluoroscopy time, were higher. Except for perforation, procedure related complications were similar between the two groups. At one year, diffuse long lesion group showed worse clinical outcomes including higher incidence of target lesions revascularization (TLR), target vessel revascularization (TVR) and TLR-major adverse cardiac events (MACE, Table).
Conclusions: Diffuse long CTO lesions needed more complex procedure techniques and devices. Further, those were associated with worse clinical outcomes at one year follow up as compared with shorter CTO lesions.
|
|
Table. Procedure related complications and one year clinical outcomes
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/CTO-length.png) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





