| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550180 93 |
| The Impact of Creatinine in Metabolic Syndrome Subjects with Normal Kidney Function |
| к≥Дл™ЕлМАнХЩкµР мЭШк≥ЉлМАнХЩ лПЩмВ∞мЭШл£МмЫР мЛђмЮ•лВік≥Љ |
| мЛ†нЩНмЫР, мµЬмГБмЫЕ, л∞∞нХЬм§А, мЭінШЄл™Е, м°∞нШДмШ•, м°∞мЬ§к≤љ, л∞ХнШХмД≠, мЬ§нШБм§А, кєАнШХмД≠, лВ®м∞љмЪ±, нЧИмКєнШЄ, кєАмЬ§лЕД, кєАкґМл∞∞ |
Backgrounds: The metabolic syndrome is a risk factor for the development of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The metabolic syndrome is independently associated with an increased risk for chronic kidney disease. The aim of this study is to know the asssociation of the metabolic syndrome and creatinine in subjects with normal kidney function.
Methods: This was a retrospective study of health examination in tertiary university hospital from January 2003, to June 2011. A total of 38,870 subjects (21,069 male and 17,801 female) were recruited. Definition of metabolic syndrome was over 3 of 5 by American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists criteria; TG > 150mg/dL, HDL < 40mg/dL (male) or < 50 mg/dL (female), systolic BP > 130mmHg or diastolic BP >85mmHg, fasting blood sugar > 100mg/dL, Body mass index >25 kg/m2. Creatinine (Cr) level was obtained from all of the subjects.
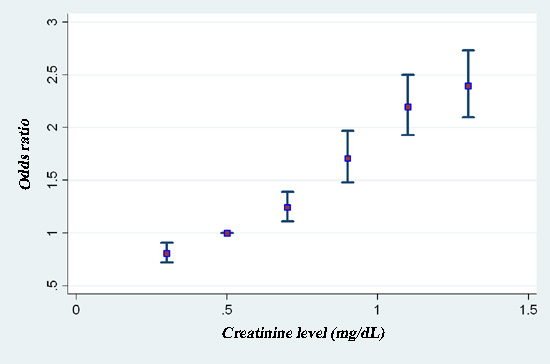
Results: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 21.0% (24.7% male and 17.6% female) for 9 years. Creatinine level was showed difference according to metabolic syndrome (0.91±0.19 vs. 0.96±0.18, p<0.001). The higher increment of 0.2 of creatinine, odd ratio of metabolic syndrome is increased 1.27 fold (p<0.01) and increased with normal kidney function by logistic regression analysis according to spline Cr.
Conclusions: The creatinine level is independently associated with an increased risk for metabolic syndrome in subjects with normal kidney function.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/MS_CR_Normal_copy.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





