| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550195 75 |
| Comparison between Drug-Eluting Stents and Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting for Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery Disease: A Pooled Analysis of Three Randomized Trials and Nine Observational Studies |
| мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА лґАмВ∞л∞±л≥СмЫР¬є , мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА нХімЪілМАл∞±л≥СмЫР¬≤ , л©Фл¶ђлЖАл≥СмЫР¬≥ , лґАмВ∞мЭШлМАвБі |
| мЮ•мЮђмЛЭ¬є , м†ХмГБл†ђ¬є , мІДнХЬмШБ¬є , мДЬм†ХмИЩ¬є , мЦСнГЬнШД¬є , кєАлМАк≤љ¬є , кєАлПЩкЄ∞¬≤ , мД§мГБнЫИ¬≤ , кєАлСРмЭЉ¬≤ , м°∞к≤љмЮД¬≥ , кєАл≥інШДвБі , л∞ХмЪ©нШДвБі , м†ЬнШХк≥§вБі , кєАлПЩмИШ¬є |
Background: The clinical outcomes for unprotected left main coronary artery (ULMCA) disease between coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and drug-eluting stents (DES) remain controversial. The objective of this study was to compare the safety and efficacy of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using DES with CABG in patients with ULMCA disease.
Methods: Databases were searched for clinical studies that reported outcomes after PCI with DES and CABG for the treatment of ULMCA disease. The end points of this meta-analysis were mortality; the composite of death, myocardial infarction, or stroke; and target vessel revascularization at 1-year follow-up. The pooled effects were calculated using fixed-effects model (Mantel-Haenszel method) or random effects models (Dersimonian and Laird method).
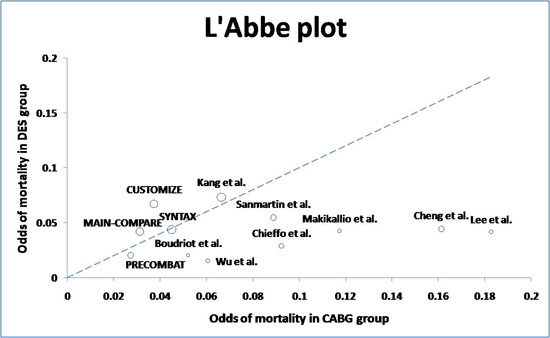
Results: Twelve clinical studies (3 randomized trials and 9 observational studies) with 5,079 patients were involved in this study. At 1-year follow-up, there was trend toward a lower risk of death (odds ratio [OR] 0.68, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.45 to 1.02, p=0.06) and the composite end point of death, myocardial infarction, or stroke (OR 0.70, 95% CI 0.49 to 1.00, p=0.05) in DES group compared to CABG group. However, target vessel revascularization was significantly higher in the DES group compared to the CABG group (OR 3.52, 95% CI 2.72 to 4.56, p<0.001). Sensitivity analysis suggested lower odds of death (OR 0.62, 95% CI 0.36 to 1.07, p=0.08) or composite endpoints (OR 0.66, 95% CI 0.40 to 1.09, p=0.10) with DES in non-randomized studies compared with those in randomized trials.
Conclusions: The results of our meta-analysis suggest that PCI with DES is associated with favorable outcomes at 1-year, as compared with CABG with marginal statistical significance in patients with ULMCA disease. In selected cases with ULMCA disease, PCI with DES is emerging as a good alternative.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/leftmainmortality.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





