| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550226 352 |
| LV Torsion and Ventricular-arterial Coupling in Hypertensive Patients |
| к≥Дл™ЕлМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР |
| кєАнШХмД≠, л∞∞нХЬм§А, мЭінШЄл™Е, мЛ†нЩНмЫР, м°∞нШДмШ•, л∞ХнШХмД≠, мЬ§нШБм§А, м°∞мЬ§к≤љ, лВ®м∞љмЪ±, нЧИмКєнШЄ, кєАмЬ§лЕД, кєАкґМл∞∞ |
Background: Vascular stiffness associated with hypertension would increase arterial elastance (Ea), whereas LV end-systolic stiffness (Ees) could be influenced by hypertensive LV hypertrophy.
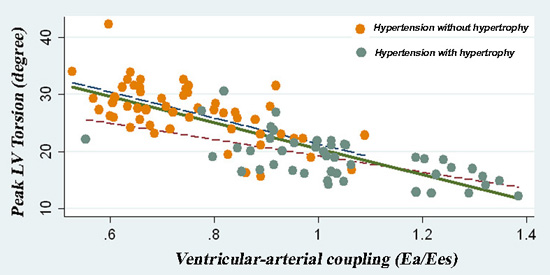
Objectives: In hypertensive patients, we investigated whether ventricular-arterial coupling (Ea/Ees) may affect LV torsion which may be an important systolic function.
Methods: Hypertensive patients without hypertrophy (n=55) and patients with hypertrophy (n=47) underwent 2D and speckle-tracking echocardiography.
Results: Hypertrophic patients had a more impaired mitral annular Doppler velocities and much lower LV torsion (18.9 vs 27.2 deg., p<0.001). While Ea was similar between two groups, Ees was significantly decreased in patient with hypertrophy, resulting into increased Ea/Ees ratio (1.03 vs. 0.75, p<0.001). Although LV torsion had significantly correlations with ejection fraction, midwall fractional shortening, LV mass index, and Ees, the correlation between LV torsion and Ea/Ees (beta=-15.2, p<0.001) was more robust in a multivariate regression analysis.
Conclusion: Abnormal LV torsion is evident in patient with hypertensive heart disease and this may be contributed by impaired Ea/Ees. The relationship of LV torsion to Ea/Ees may provide a better fundamental understanding of the hypertensive hypertrophy.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/VAC.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





