| ЙпЧЅЧќНФ : РўРКПЌБИРкЛѓ
|
СЂМіЙјШЃ - 550246 6 |
| Noninvasive diagnosis of ischemia-causing coronary stenosis using coronary CT angiogram (CCTA):
Comparison of transluminal attenuation gradient (TAG) and fractional flow reserve computed from
CCTA (FFRCT) |
| ььИыэъЕыГь ьЌэъДьМэАТЙ , ььИьМьБыГь ьЌэъДьМэАТВ, ьььэъГМТГ , ыЖыЙььИыэъЕыГь ьЌэъДьМэАтД |
| ьЄьАьДТЙ, ьЕьЇэИТВ, ъЙьЇэТЙ, ьэыЊЈТЙ, ыАъВНьАТЙ , ъАэьЌТЙ, ьЁАъЕЌьтД, ъЙьЉьЇТЙ, ъЕЌыГИъЖТЙ, ъЖэьВ ТВ, ьЕьАэТГ, ьЕыьЃМтД,ъЙэЈьТЙ, ьЄыГэЌТЙ, ыАьыААТЙ |
Background
Although coronary CT angiography (CCTA) is commonly used to detect coronary artery disease (CAD), it can't reliably assess the functional significance of CAD. Novel technologies based on CCTA were developed to integrate anatomical and functional assessment, however, the diagnostic performance of these methods has never been compared. In this study, we compared the diagnostic performance of CCTA-derived computed fraction flow reserve (FFRCT) and transluminal attenuation gradient (TAG) for the diagnosis of lesion-specific ischemia.
Methods 53 consecutive patients who underwent CCTA, coronary angiography with FFR measurement were included. Independent core laboratories determined CAD severity by CCTA, TAG, and FFRCT. TAG was defined as the linear regression coefficient between intraluminal radiological attenuation (HU) and length from the ostium (mm). FFRCT were computed from CCTA data using computational fluid dynamics technology.
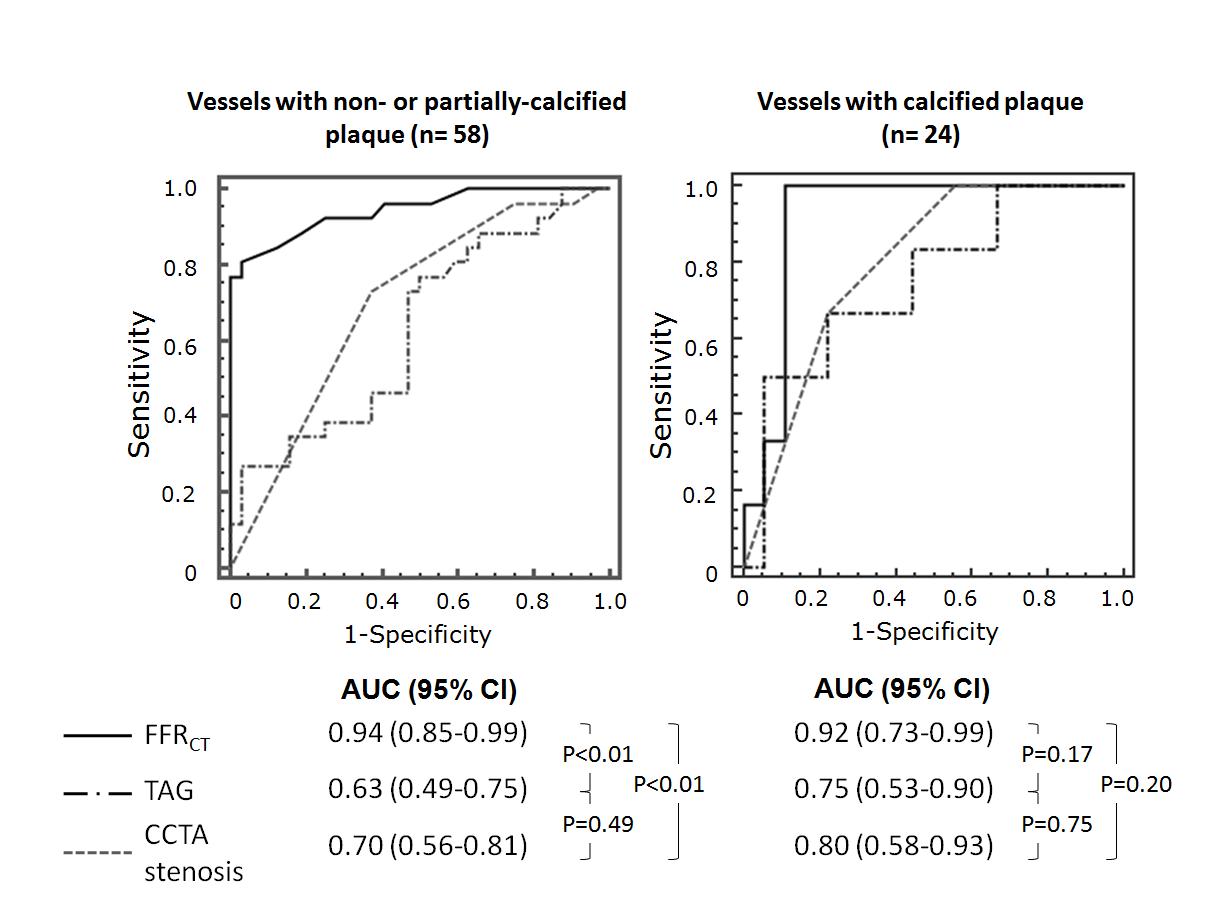
Results Among 82 vessels, 32 (39%) had ischemia causing stenosis by invasive FFR (FFRтЄ0.80). Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of TAG (тЄ-0.654) for detection of ischemia causing stenosis were 38%, 88%, 67% and 69%, while those of FFRCT (тЄ0.77) were 81%, 94%, 90%, and 89%, respectively. ROC curve analysis showed a significantly larger area under the curve (AUC) for FFRCT (0.94) compared to that for TAG (0.63, p<0.01) and CCTA stenosis (0.73, p<0.01) in overall group. In vessels with non-calcified plaque or partially calcified plaque, FFRCT showed a larger AUC (0.94) compared to that of TAG (0.63, p<0.01) or CCTA stenosis (0.70, p<0.01). Whereas, in vessels with calcified plaque, AUC of FFRCT (0.92) is comparable to that of TAG (0.75, p=0.17) or CCTA stenosis (0.80, p=0.20) (Figure)
Conclusions Noninvasive FFR computed from CCTA provides better diagnostic performance for diagnosis of lesion-specific ischemia compared to CCTA stenosis and TAG.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/FigureFinal.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





