| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550302 117 |
| Impact of High On-Treatment Platelet Reactivity on Periprocedural Myocardial Infarction in Patients Undergoing Drug-Eluting Stents Implantation |
| лґАмВ∞ л∞±л™ЕмЫР¬є, нХімЪілМА л∞±л≥СмЫР ¬≤ |
| м†ХмГБл†ђ¬є , мЮ•мЮђмЛЭ¬є , мІДнХЬмШБ¬є ,мДЬм†ХмИЩ¬є ,мЦСнГЬнШД¬є ,кєАлМАк≤љ¬є ,кєАлПЩкЄ∞¬≤ ,кєАкЄ∞нЫИ¬≤, мД§мГБнЫИ¬≤ ,кєАлСРмЭЉ¬≤ ,кєАлПЩмИШ¬є |
Background: Inadequate platelet inhibition after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has been advocated to explain higher risk of adverse cardiac outcomes. We sought to evaluate the impact of platelet reactivity after clopidogrel, as assessed by VerifyNow point-of-care assay (Accumetrics, San Diego, California), on myonecrosis in patients undergoing PCI with drug-eluting stents.
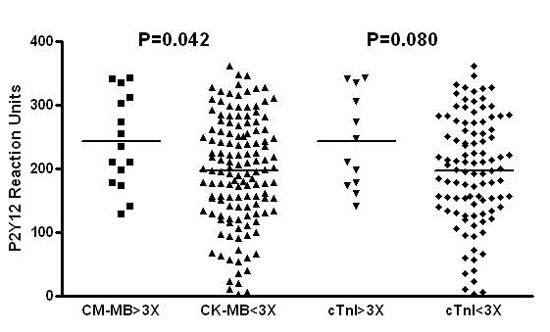
Methods: A total of 148 consecutive cardiac biomarker-negative patients treated with clopidogrel and undergoing elective PCI were enrolled. Creatine kinase–myocardial band isoenzyme (CK-MB) and cardiac troponin I (cTnI) were measured before and monitored every 6 hours after PCI. Platelet reactivity after clopidogrel was assessed immediately before PCI by the VerifyNow P2Y12 point-of-care assay. Clopidogrel response was measured with P2Y12 reaction units (PRU) and percent inhibition P2Y12 from baseline (percent inhibition P2Y12) and aspirin response with aspirin reaction units (ARU). High on-treatment platelet reactivity (HOPR) after clopidogrel was defined as a platelet reaction unit (PRU) вЙ•240.
Results: PRU values were higher in patients with periprocedural myocardial infarction (PMI), with statistical significance with regard to CK-MB elevation (243 ± 73 vs. 196 ± 85, p=0.042), and by trend with regard to cTnI elevation (243 ± 75 vs. 197 ± 85, p=0.080). Patients with HOPR showed more frequent PMI, both by CK-MB (13.7% vs. 8.2%, p<0.001) and cTnI definition (15.4% vs. 8.2%, p<0.001). Patients with percent inhibition P2Y12 <20% developed significantly higher incidence of PMI (18.4% vs. 7.3%, p=0.050). There was no significant differences in ARUs in patients with or without PMI, neither by CK-MB (411 ± 36 vs. 407 ± 55, p=0.786) nor by cTnI definition (404 ± 21 vs. 406 ± 57, p=0.883).
Conclusion: HOPR after clopidogrel is closely related with increased risk of PMI in patients undergoing PCI with drug-eluting stents.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/HOPRPPM.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





