| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550316 304 |
| Sodium Bicarbonate Therapy for the Prevention of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis |
| мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА лґАмВ∞л∞±л≥СмЫР¬є , мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА нХімЪілМАл∞±л≥СмЫР¬≤ , л©Фл¶ђлЖАл≥СмЫР¬≥ , лґАмВ∞мЭШлМАвБі |
| мЮ•мЮђмЛЭ¬є , м†ХмГБл†ђ¬є , мІДнХЬмШБ¬є , мДЬм†ХмИЩ¬є , мЦСнГЬнШД¬є , кєАлМАк≤љ¬є , л∞Хл≥ілѓЉ¬≤ , кєАлПЩкЄ∞¬≤ , кєАкЄ∞нЫИ¬≤ , мД§мГБнЫИ¬≤ , кєАлСРмЭЉ¬≤ , м°∞к≤љмЮД¬≥ , кєАл≥інШДвБі , л∞ХмЪ©нШДвБі , м†ЬнШХк≥§вБі , кєАлПЩмИШ¬є |
Background: Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is one of the leading causes of in-hospital acute renal failure. Sodium bicarbonate has been postulated to prevent CIN by various mechanisms. However, there have been conflicting reports on the use of intravenous sodium bicarbonate for prevention of CIN.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane databases for randomized controlled trials that compared sodium chloride with sodium bicarbonate hydration regimen regarding CIN. The pooled effects were calculated using random effects models (DerSimonian and Laird method).
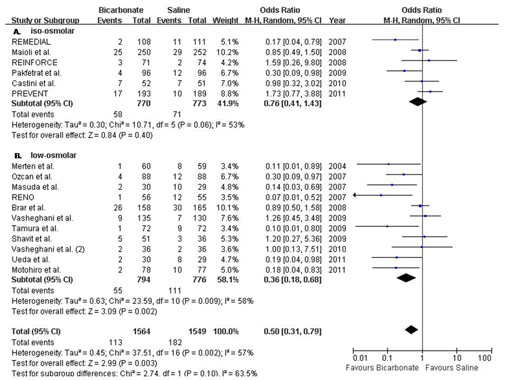
Results: Data were combined across 17 clinical trials consisting of 3,113 patients. Pre-procedural hydration with sodium bicarbonate was associated with a significant decrease in the rate of CIN (odds ratio [OR] 0.50; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.31-0.79, p=0.003). Stratified analyses by the type of contrast medium used suggested lower odds of CIN with sodium bicarbonate in studies using low-osmolar contrast media (OR 0.36; 95% CI 0.18-0.68, p=0.002) compared with those using the iso-osmolar agents (OR 0.76; 95% CI 0.41-1.43, p=0.40). No significant difference in the rates of post-procedure death (OR 0.49; 95% CI 0.23-1.04, p=0.06) and the requirement for renal replacement therapy (OR 0.80; 95% CI 0.38-1.70, p=0.56) was observed.
Conclusions: This updated meta-analysis demonstrates that sodium bicarbonate-based hydration is superior to sodium chloride in prevention of CIN and should be considered the optimal hydration strategy especially in patients undergoing exposure to iodinated contrast.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/cinfigure.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





