| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550322 347 |
| Radial versus Femoral Approach for Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention In Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: An Updated Meta-analysis |
| мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА лґАмВ∞л∞±л≥СмЫР¬є , мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА нХімЪілМА л∞±л≥СмЫР¬≤ , л©Фл¶ђлЖАл≥СмЫР¬≥ , лґАмВ∞мЭШлМАвБі |
| мЮ•мЮђмЛЭ¬є , м†ХмГБл†ђ¬є , мІДнХЬмШБ¬є , мДЬм†ХмИЩ¬є , мЦСнГЬнШД¬є , кєАлМАк≤љ¬є , л∞Хл≥ілѓЉ¬≤ , кєАлПЩкЄ∞¬≤ , кєАкЄ∞нЫИ¬≤ , мД§мГБнЫИ¬≤ , кєАлСРмЭЉ¬≤ , м°∞к≤љмЮД¬≥ , кєАл≥інШДвБі , л∞ХмЪ©нШДвБі , м†ЬнШХк≥§вБі , кєАлПЩмИШ¬є |
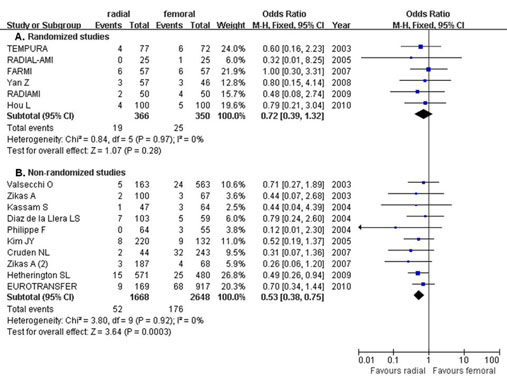
Background: There is an increasing amount of data suggesting that radial approach is associated with lower incidence of complications in vascular access site and improved clinical outcomes compared with femoral approach in the setting of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The objective of this study was to assess the safety and efficacy of radial versus femoral percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for patients with STEMI.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane databases for randomized, case-control, and cohort studies comparing access-related complications and clinical outcomes from January 2001 to May 2011. The pooled effects were calculated using fixed-effects model (Mantel-Haenszel method) or random effects models (Dersimonian and Laird method).
Results: Seventeen studies involving 6,248 patients were identified. Transradial PCI was associated with a significant reductions in the composite of death, myocardial infarction, or stroke (odds ratio [OR] 0.57, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.42 to 0.76, p<0.001) and mortality (OR 0.63, 95% CI 0.46 to 0.85, p=0.003). Transradial PCI reduced major bleeding compared to transfemoral PCI (OR 0.29, 95% CI 0.17-0.49, p<0.001). Stratification and sensitivity analysis suggested lower odds of death or composite endpoints with transradial approach in non-randomized studies compared with those in randomized trials (Figure).
Conclusions: This updated meta-analysis demonstrates that transradial PCI reduces the risk of significant periprocedural bleeding and improve clinical outcomes in patients with STEMI.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/transradialkorean.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





