| єя«•«ьљƒ : Clinical award session
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550856 8 |
| Regular supervised exercise training improves endothelial function, early atherosclerosis, arterial stiffness and endothelial progenitor cells in PCI patients. |
| к≥†лМА мХИмХФ л≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞ лВік≥Љ |
| л∞ХмЮђнШХ, м†ХмИШмІД, кєАмҐЕнШЄ, л∞ХмєШмЧ∞, мµЬмІАнШД, мЭікЈАмИЩ, мµЬмКєм≤†, кєАм†ЬмГБ, мХИм≤†лѓЉ, нЩНмИЬм§А, мЮДлПДмД† |
Backgrounds
A disrupted balance between endothelial injury and repair induces endothelial dysfunction and endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) augment vascular repair. So, exercise improves endothelial function through increased numbers of EPC. We investigated the effect of training on vascular health by measuring the number of circulating EPC, and assessing flow-mediated dilation (FMD), brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) and carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) in patients with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Methods
Fifty-nine patients who were done PCI recently were randomized to full medical treatments or additional 3 months regular supervised exercise program (4 times a week, 1 hr a day). FMD, baPWV, carotid IMT, HOMA, hs-CRP and lipid profiles were measured and circulating CD34/KDR, CD34/CD117 and CD34/CD133 EPC were quantified by flow cytometry at baselines and after 3 months.
Results
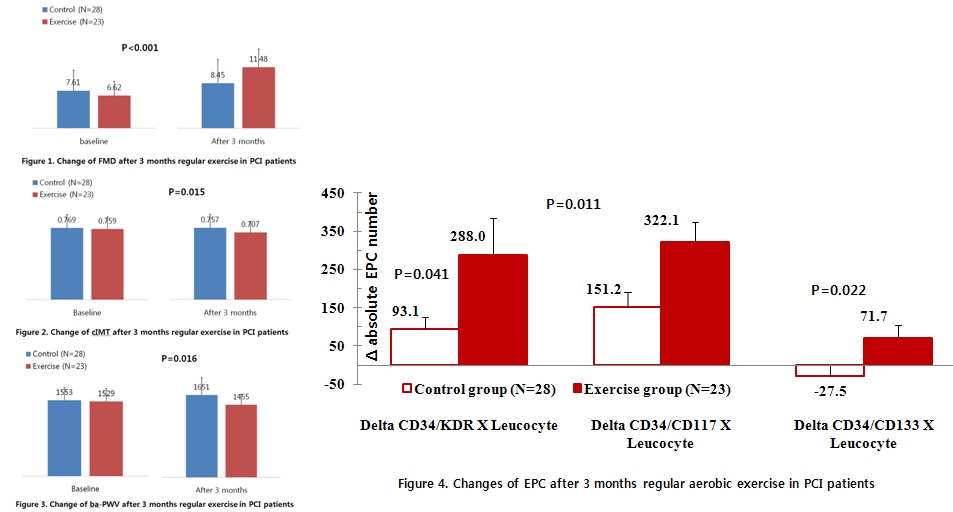
Finally 23 patients joined exercise program(control, N=28). There was no significant difference of baseline characteristics and medication between 2 groups. After 3 months, FMD improved significantly in exercise group (6.62% to 11.48%) compared with control group (7.61% to 8.45%) (P<0.001) (fig 1). Carotid IMT reduced significantly in exercise group (0.759mm to 0.707mm) compared with control group (P=0.015) (fig 2). ba-PWV reduced significantly in exercise group (1529cmm/s to 1455 cmm/s) compared with control group (P=0.016) (fig 3). Numbers of CD34/KDR, CD34/CD117 and CD34/CD133 EPCs increased significantly after exercise compared with control group (P= 0.041, 0.011, 0.022, respectively) (fig 4). We also could see to reduce waist to hip ratio in exercise group compared with control group (P<0.001).
Conclusions
Three months regular supervised exercise improved FMD, ba-PWV, carotid IMT and waist to hip ratio in PCI patients. and it augmented numbers of circulating EPCs. Our results showed that exercise contributes to additional improvement of vascular health in PCI patients with optimal medical treatments.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/eveff.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





