| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550888 396 |
| Embotic burden degree in acute pulmonary embolism is correlated with D-dimer and PASP |
| лМАкµђ к∞АнЖ®л¶≠ лМАнХЩл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞ лВік≥Љ |
| нЩНмКєнСЬ, кєАл≥СкЈЬ, мЖРмЮРмШБ, мЭімШБмИШ, мЭімІДл∞∞, л•ШмЮђкЈЉ, мµЬмІАмЪ©, кєАкЄ∞мЛЭ, мЮ•мД±кµ≠ |
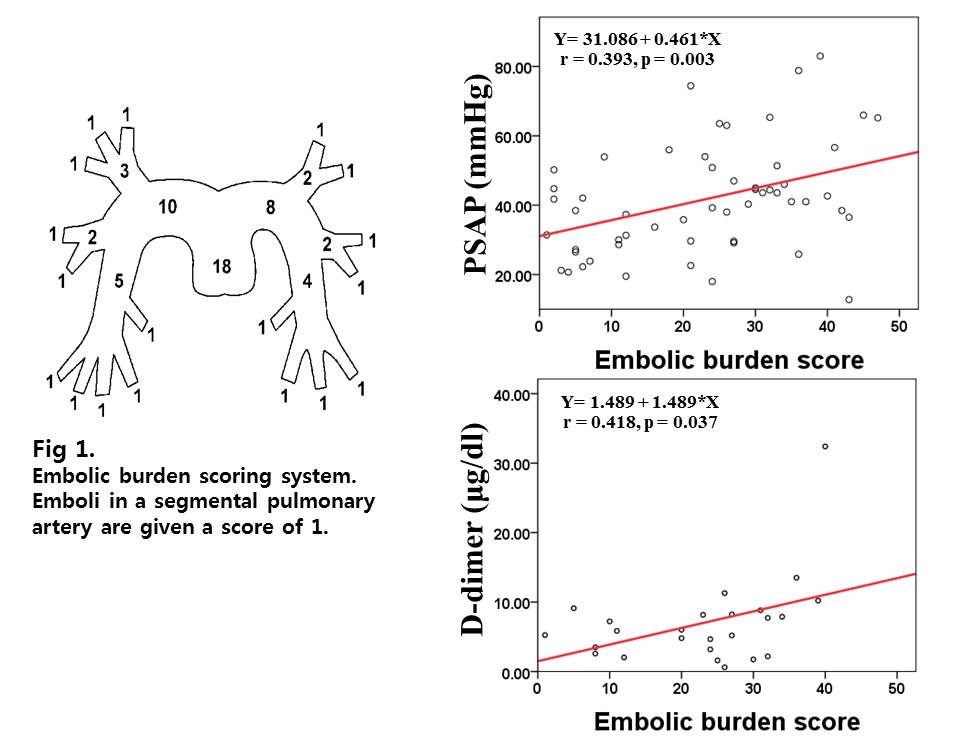
Purpose: Embolic burden degree in acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was known to be associated with disease severity and prognosis. The aim of the study was to assess the correlation with laboratory biomarkers, echocardiographic parameters and Computed Tomography (CT) pulmonary angiographic embolic burden score in acute PE. Method: A total of 103 patients (mean age: 63.9years, male 35.9%) with acute PE were investigated. CT pulmonary angiographic embolic burden scoring system was based on the number of segmental pulmonary arteries involved, with weight added to an occlusive thrombus (Fig 1). All patients had blood drawn to measure levels of emerging biological markers before pulmonary angiography was performed. All patients was performed the echocardiogram within 7 days after diagnosis of PE. Result: Pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP, R=0.393, P=0.037) and D-dimer values (R=0.418, P=0.037) were significantly increased according to the CT pulmonary angiographic embolic burden score. But, there is no correlation between CT pulmonary embolic burden score and risk of death due to PE (P=0.929). Conclusion: Embolic burden degree in acute pulmonary embolism show positive correlation with D-dimer and PASP. But, embolic burden degree was not associated with risk of death due to PE. But, for more reliable result more larger study and randomized control study were required.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/PTE.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





