| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550908 251 |
| Efficacy and Safety of Adjuvant Proximal Balloon Inflation Comprising Stent Proximal Edge for Full Expansion of the Stent by Stent Balloon |
| к≥†л†§лМАнХЩкµР кµђл°Ьл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ |
| мµЬл≥Ск±Є, лВШмКємЪі, Amro Elnagar, лВШмІДмШ§, мµЬм≤†мЫЕ, мЮДнЩНмЭШ, кєАмІДмЫР, кєАмЭСм£Љ, нХЬмД±мЪ∞, л∞Хм∞љкЈЬ, мДЬнЩНмДЭ, мШ§лПЩм£Љ |
Background: Another shorter & bigger non-compliant balloon is being used for optimal expansion of the stent, particularly the proximal portion of the stent when the proximal and distal reference vessel diameters are significantly different. The safety and efficacy of adjuvant proximal balloon inflation (PBI) comprising proximal edge of the stent using stent balloon with higher inflation pressure are largely unknown. This strategy was intended to reduce procedural time, contrast amount and cost when we do the adjuvant ballooning for optimal stent expansion.
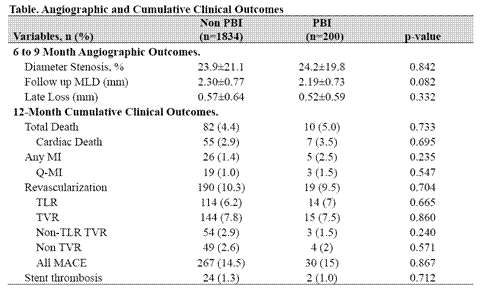
Methods: This study consisted of 2164 consecutive patients (pts) underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents (DESs) from January 2004 to April 2010. A total 211 pts (259 lesions) have performed PBI using same stent balloon. Six-month angiographic and twelve-month clinical outcomes were compared between the PBI group and non-PBI group.
Results: The baseline clinical and procedural characteristics were well balanced between the two groups, except that the left circumflex lesions were more common in the PBI group. There was no difference in procedural success rate and in hospital complications between the two groups, except that the incidence of peri-procedural myocardial infarction (MI, 5.8% vs. 10.4%, P<0.001) was higher in the PBI group. At 6-month, the follow up minimal luminal diameter (MLD) was smaller in the PBI group. However, this angiographic benefit was not translated into the clinical benefit up to 12 months. (Table).
Conclusion: PBI was associated with higher incidence of peri-procedural MI but other safety profiles, procedural success, in-hospital complications, mid-term angiographic and clinical outcomes were similar with those of non-PBI group. PBI can be a cost-effective strategy when the proximal and distal reference vessel diameters are significantly different at the time of stent implantation.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/PBI.gif) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





