Heart Failure 1
Digital Heath Intervention to Optimize HF Management

Minjae Yoon, MD .
Seoul National Univ., KoreaHeart failure (HF) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, despite the proven benefits of guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT). A persistent gap between recommendations and clinical practice, driven by therapeutic inertia and systemic barriers, contributes to suboptimal outcomes. Digital health interventions have emerged as a powerful approach to address these challenges, enabling accelerated initiation, titration, and long-term adherence to GDMT, while facilitating remote patient monitoring.
Digital solutions are fundamentally reshaping HF care delivery by strengthening clinician support and enabling proactive therapy optimization. Remote patient monitoring is a central component, continuously capturing key vital signs such as weight, blood pressure, and heart rate to provide real-time data for clinical decision-making. When implemented through nurse- or pharmacist-led teams using standardized titration protocols, remote patient monitoring facilitates rapid and safe uptitration of GDMT, enabling patients to achieve target doses more efficiently and with fewer adverse events than under conventional approaches. Beyond monitoring, remote consultation platforms extend access to specialist input, particularly in resource-limited settings, while clinical decision support systems embedded in electronic health records deliver timely, evidence-based prompts. Multifaceted programs combining these tools are most effective, highlighting the need for coordinated digital ecosystems.
Equally important is the role of digital tools in patient engagement. Educational modules, medication checklists, and mobile applications not only enhance patient knowledge but also provide biofeedback on symptoms and quality of life. This empowerment fosters adherence, strengthens communication with care teams, and aligns treatment decisions with patient priorities. Combining clinician support with patient activation creates a more comprehensive and sustainable model of HF management.
In summary, digital health interventions offer a powerful framework to optimize HF treatment. Through remote monitoring, virtual consults, and patient-centered engagement platforms, these solutions overcome logistical barriers and enable more proactive, guideline-concordant care. Remaining challenges—such as disparities in digital literacy, equitable access, and integration into clinical workflows—must be addressed, but accumulating evidence suggests that digital innovations can significantly improve outcomes. Future research should focus on scalability, long-term safety, and effectiveness to ensure that the promise of digital health is fully realized across diverse patient populations.
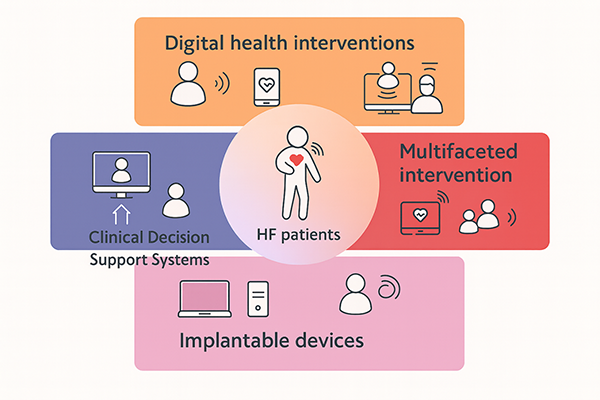
Figure 1. Digital solutions in HF management
